

This article covers the specifics of what they do. In addition, we emphasize the importance of clinical suspicion in diagnosing KFD due to the fact that axillary involvement of KFD is extremely rare.Īxilla COVID-19 Vaccines Histiocytic Necrotizing Lymphadenitis Kikuchi-Fujimoto’s disease Lymphadenopathy Ultrasonography. The covid vaccines are very negative for one’s immune system and several organs. Through this case report, we highlight that KFD should be considered in the differential diagnosis of patients with axillary lymphadenopathy who have undergone COVID-19 vaccination, as unusual side effects of COVID-19 vaccination have been increasingly reported in the literature owing to the rapid development of various COVID-19 vaccines during the pandemic period. From these reports the most common side effects likely to be linked to the vaccines are headache, muscle and joint pain, fever, chills and nausea. To quantify the pooled rate and risk ratio of seroconversion following the uncomplete, complete, or booster dose of COVID-19 vaccines in patients living with HIV. In this case, we suspected the lesions as COVID-19 vaccination-related lymphadenopathy on the initial ultrasonographic examination. Conclusion: Through this case report, we highlight that KFD should be considered in the differential diagnosis of patients with axillary lymphadenopathy who have undergone COVID-19 vaccination, as unusual side effects of COVID-19 vaccination have been increasingly reported in the literature owing to the rapid development of various COVID-19.
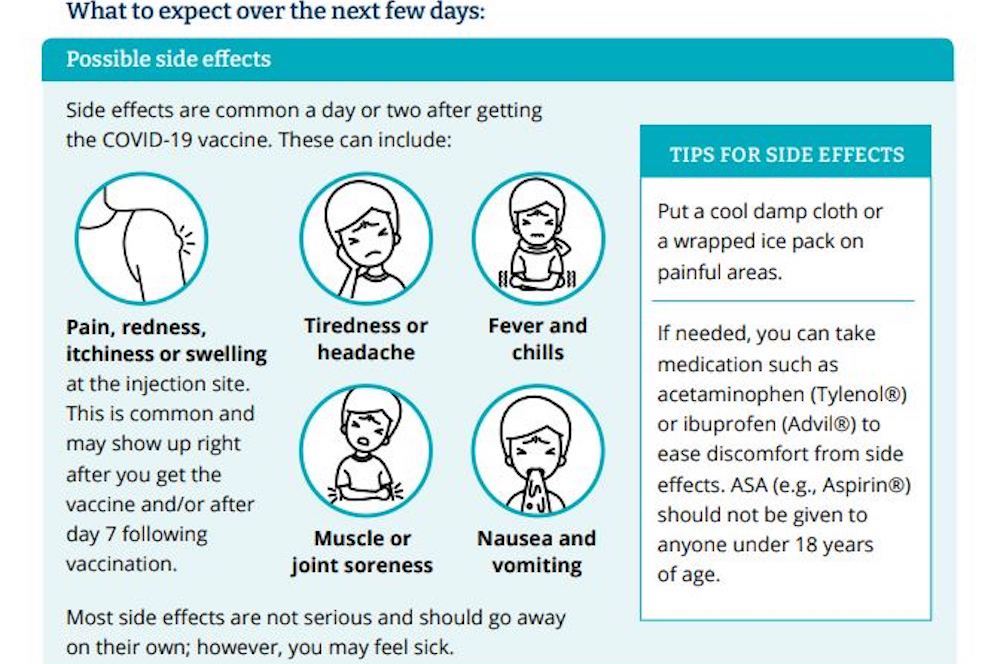
We report on a case of KFD that presented 3 weeks after receiving the messenger ribonucleic acid-based coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccine. The most common side effects of the COVID-19 vaccine are: pain, itching or swelling in the arm, tiredness, nausea, headache, muscle aches, or a moderate fever.

KFD commonly involves the posterior cervical region and very rarely occurs in the axilla. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease (KFD) is a rare, self-limiting inflammatory condition of unknown etiology that is characterized by fever and painful lymphadenopathy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
